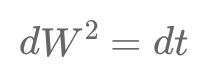Processus et Modèles Stochastiques · 09. octobre 2023
Quantitative finance relies on rules from stochastic calculus, like dW^2=dt, highlighting Brownian motion's unpredictability, and Zero Rules, underscoring infinitesimal term behaviors, crucial in financial modeling and risk management.
#Finance #RiskManagement
Processus et Modèles Stochastiques · 09. octobre 2023
Les règles de multiplication en calcul stochastique sont fondamentales pour modéliser les processus aléatoires, tels que le mouvement brownien, en finance quantitative. Elles permettent de comprendre les comportements de variance et d'incertitude, essentiels dans l'évaluation des options et la gestion des risques.
Processus et Modèles Stochastiques · 17. septembre 2023
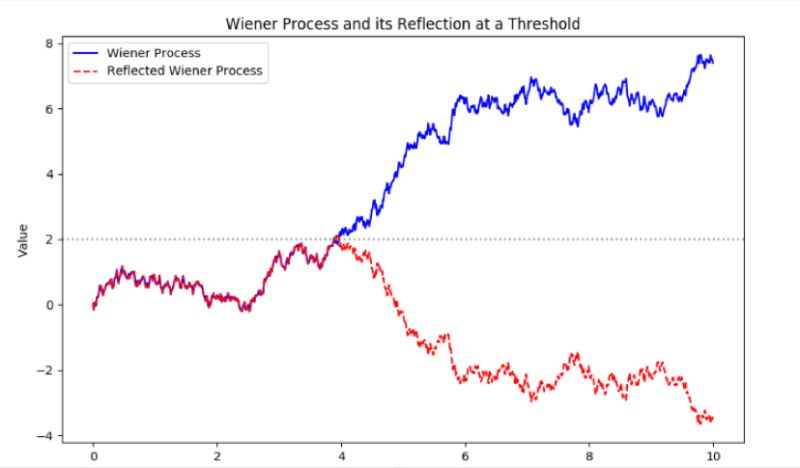
The reflection principle, illustrated by a stone's path and reflection in a lake, mirrors the Wiener process in stochastic calculations, highlighting symmetry in Brownian motion. It simplifies math in stochastic process problems, aiding in pricing barrier and lookback options. #SEO
08. juillet 2023
The Black-Scholes partial differential equation in layman’s terms…
#OptionPricing, #BlackScholes, #FinancialModeling, #QuantitativeFinance, #RiskNeutralMeasure
Stochastic Models and Processes · 04. février 2023
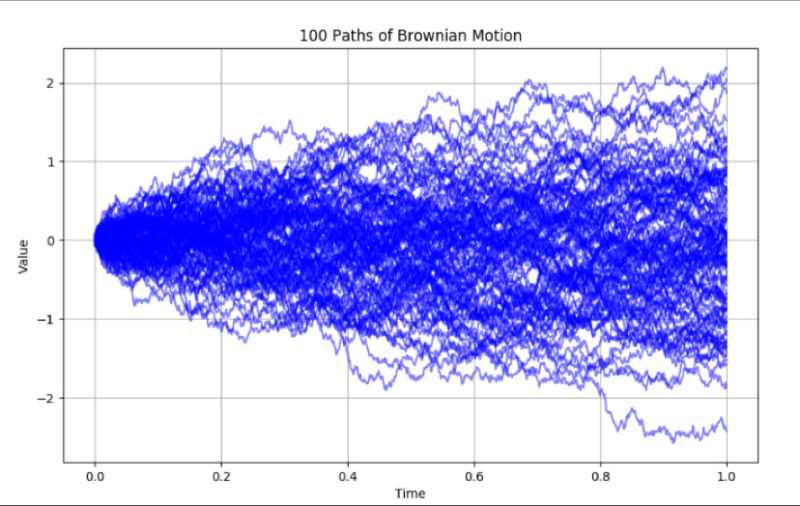
Brownian motion, a cornerstone of stochastic processes, represents the seemingly random movement of particles in a liquid or gas. Named after botanist Robert Brown, who observed the erratic motion of pollen grains in water, it serves as a vital model in various fields, including the renowned Black-Scholes model for option pricing in finance.