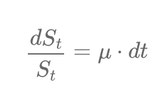
Step 1 - Given Equation:
The equation \( \frac{dS}{dt} = \mu \cdot S_t \) tells us something important: it shows that during a tiny moment, the change in the price of an asset (like a stock) is equal to a certain number \( \mu \) (we call it the "drift") multiplied by the asset's current price \( S_t \).
Step 2 - Dividing Both Sides:
If we divide both sides of the equation by \( S_t \) (the asset's current price), and then multiply both sides by a tiny amount of time \( dt \), we get:
$$\frac{dS_t}{S_t} = \mu \cdot dt$$
This equation is important because it links how the percentage change in the asset's price relates to the drift \( \mu \) and the tiny time step \( dt \).
Step 3 - Solving the Differential Equation:
Now we're going to solve this equation. Think of it like solving a puzzle to find out how the asset's price changes over time. By integrating the right side of the equation (which means adding up all the small changes), we get:
$$\ln(S_t) + c_1 = \mu \cdot t + c_2$$
Note: If you differentiate \( \ln(S_t) \) with respect to \( S_t \), you get \( \frac{1}{S_t} \).
Step 4 - Simplifying and Antilog:
If we subtract \( c_1 \) from both sides of the equation, we get:
$$\ln(S_t) = \mu \cdot t + (c_2 - c_1)$$
Now, let's use a special operation called "antilog" on both sides. It's like the opposite of taking the natural logarithm. This operation turns \( \ln(S_t) \) back into \( S_t \).
Step 5 - Getting the Final Equation:
By using the antilog on both sides, we get:
$$S_t = e^{\mu t + c_2 - c_1}$$
We can simplify \( c_2 - c_1 \) into just \( c \) (a single number).
Step 6 - Wrapping It Up:
When we have \( c = c_2 - c_1 \), and we set \( e^c \) equal to the initial price \( S_0 \), the equation becomes:
$$S_t = S_0 \cdot e^{\mu t}$$
This means that the future price of the asset is the initial price times \( e \) raised to the power of the drift \( \mu \) times \( t \).
In simpler terms, the equation helps us predict how the asset's price changes over time using a drift rate \( \mu \). It's like having a math formula to see how an asset's price will grow over time based on a constant rate of change.

Écrire commentaire